Minimax approximation
The approximate function minimizes approximation error in a discrete least-squares sense. By following up with an iteratively reweighted least-squares (IRLS) approach initially due to Lawson [2, 7], we can approach the classical problem of optimization in the infinity- or max-norm sense instead.
For example, suppose we limit the degree of a rational interpolant of a smooth function:
using RationalFunctionApproximation, CairoMakie
const shg = current_figure
f = x -> exp(cos(4x) - sin(3x))
r = approximate(f, unit_interval, max_iter=12)Barycentric{Float64, Float64} rational of type (11, 11) constructed on: Segment(-1.0,1.0)The error varies a lot in amplitude over the interval:
errorplot(r)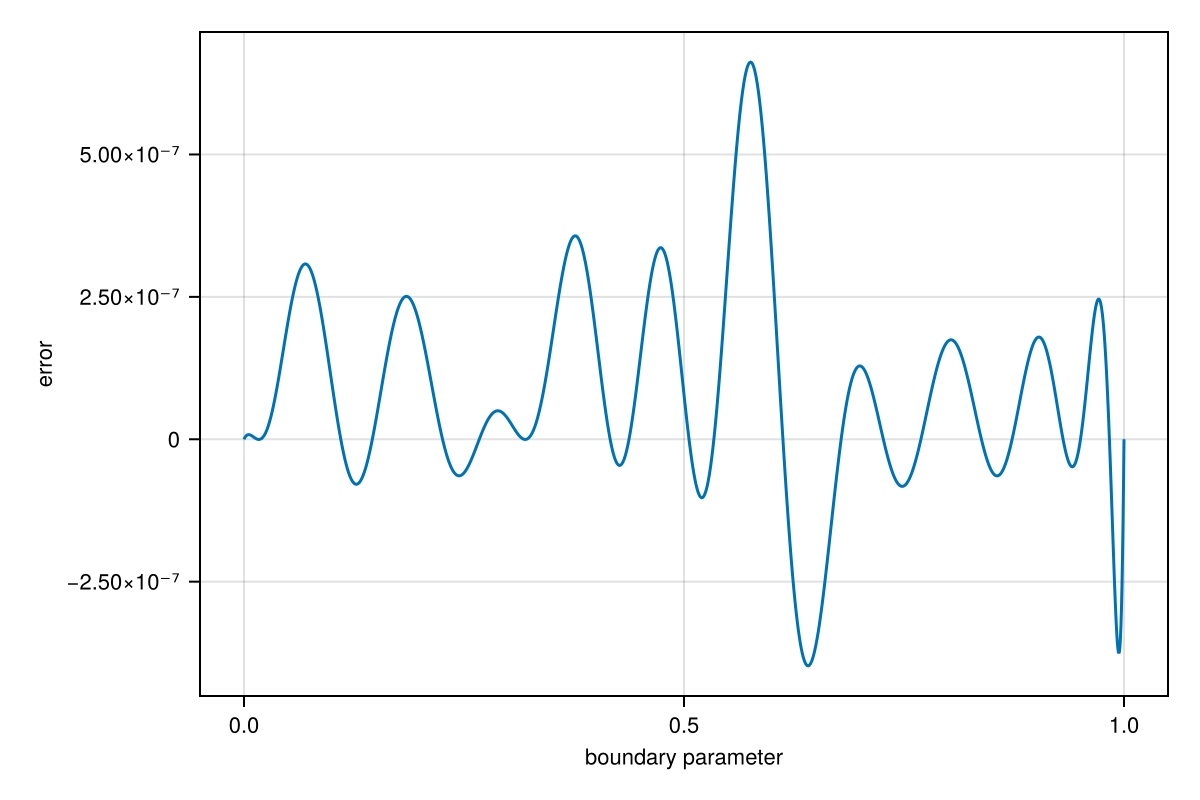
Now we apply 20 Lawson iterations to refine the approximation and approach the minimax ideal:
r = minimax(r, 20)
errorplot(r)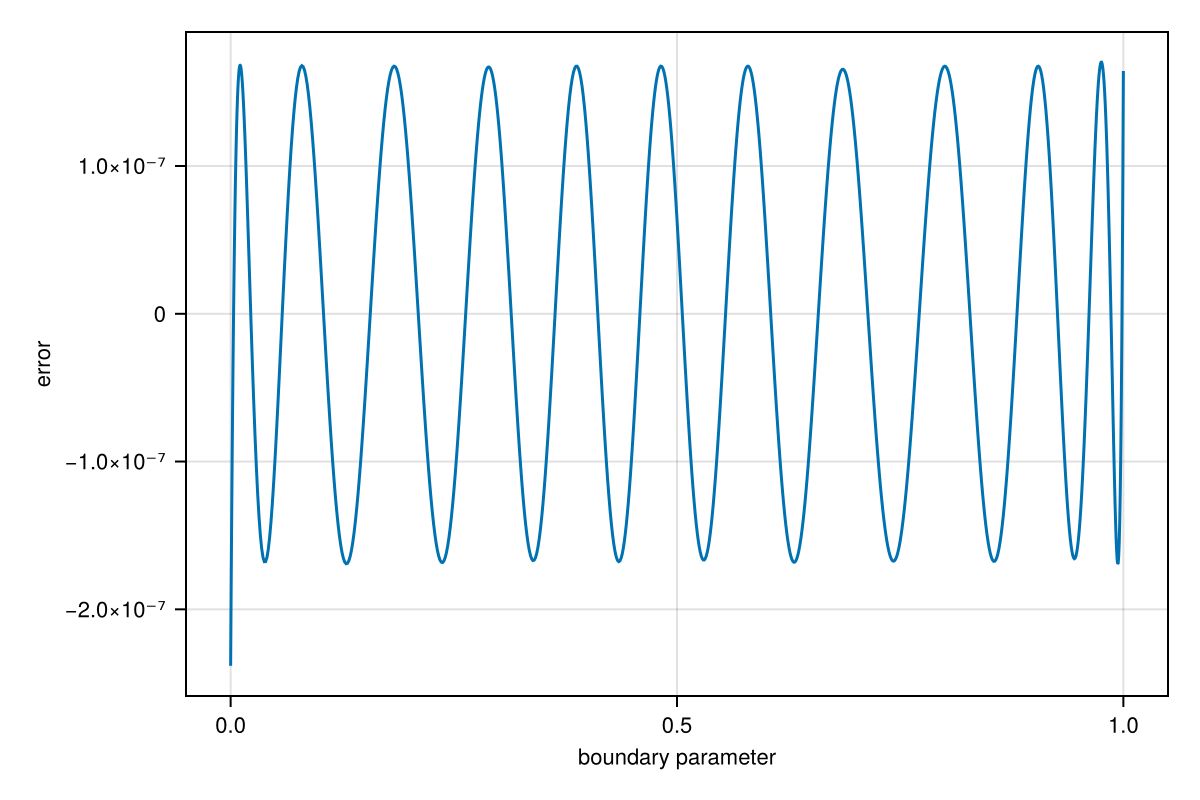
As you can see above, the error is now nearly equioscillatory over the interval. Moreover, the interpolation nodes appear to have shifted to resemble Chebyshev points of the first kind. But if we try minimax approximation on the unit circle, max-norm approximation tends to lead to equally spaced nodes:
f = z -> cos(4z) - sin(3z)
r = approximate(f, unit_circle, max_iter=10)
r = minimax(r, 20)
errorplot(r, use_abs=false)